In this blog post we explain what is conflict and its definition, characteristics, types and managing techniques. let’s first understand what does conflict mean?
What is Conflict?
Definition of Conflict: Conflict is the process of any disagreement between two or more people or groups. Whenever two or more people have incompatible interests, different values, goals, and understanding conflict arises. It may arise within a person, within people, groups, or within organizations.
Conflicts are all those kinds of opposition or antagonistic interaction between individuals or among groups that form some kind of friction, disagreement, or discord arising within them.
When the beliefs or actions of one or more members of a group are resisted by or unacceptable to another group, conflict arises. It exists in such scenarios where one party perceives that another party has hampered or might be able to hamper their accomplishment of goals.
Characteristics of Conflict
1. Conflict is a Process
Conflict is a process and occurs in layers. First is always the ‘layer of misunderstanding’. Other layers are differences of values, viewpoint, interest, and even interpersonal differences.
Conflict is called a process because it begins with the first party perceiving the other party to oppose or negatively affect its interests. This process ends with competing, compromising, collaborating, or avoiding.
2. Conflict is Inevitable
Conflict exists everywhere. No two people are alike. Hence, they may have individual differences. These differences may be because of values or otherwise, leading to conflict. Conflict is inevitable and often for the good, and it can be minimized, diverted and/or resolved.
3. Conflict is a Normal Part of Life
Individuals, groups, and business organizations have unlimited needs and different values. Their limited resources and incompatibility lead to conflicts. Conflict is not a problem if it is managed properly.
4. Perception
Conflict must be perceived by the parties, otherwise it does not exist. What we perceive and think affects our behavior, communication, and attitudes.
5. Opposition
One party involved in the conflict must be perceiving or doing something that the other party does not like or want.
6. Interdependence and Interaction
Conflict must include some kind of real or perceived interdependence. Without interdependence, there will be no interaction. Conflict will occur only when some kind of interaction takes place.
7. Conflict is Multidimensional
It comes in different ways in accordance with degree of capacity and seriousness. At times, it may even improve difficult situations.
Types of Conflict
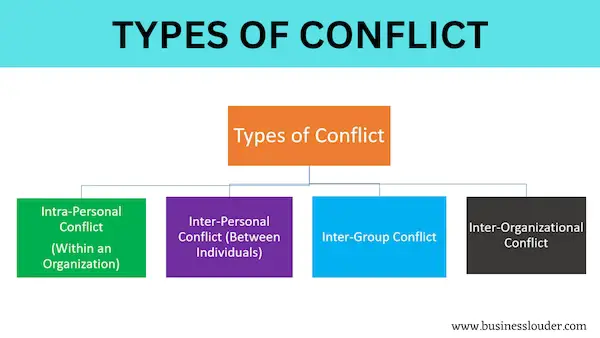
There are 4 types of conflict, namely –
1. Intra-Personal Conflict (inside an Individual)
Intra-personal conflict arises within an individual, due to divergent goals and multiple roles, that the individual is expected to play.
Goal conflicts arise when an individual faces the problem of choosing among many competing goals. Role conflicts occur when the expectations of an individual’s role are materially different or opposite and the individual can meet a particular expectation only at the cost of other expectations. It might also occur due to role ambiguity. Role ambiguity occurs when an individual is not clear about his duties and responsibilities.
2. Interpersonal Conflict (among individuals)
Interpersonal conflict occurs when two or more persons interact with each other. Such interaction may take place between peers or between seniors and subordinates.
The conflict between them might arise due to differences in the choices made by them. It occurs as a result of an individual’s inability to conform to the norms of the group.
The main causes of this conflict are – personality differences, perceptions, power and status differences, clash of values and interests, scarcity of resources, etc.
3. Inter-Group Conflict
Such conflict occurs between two or more groups in an organization. Intergroup conflicts arise for organizational causes rather than interpersonal purposes.
Conflicts between production and sales departments, between management and unions, are examples of inter-group conflicts. The major reasons for such conflicts are competition for scarce resources, task interdependence, joint decision-making, introduction to change, and incompatible goals.
4. Inter-Organizational Conflict
This type of conflict arises between two organizations, as a result of business competition. Both conflicting parties usually engage in providing similar types of products or services. As a result, both parties become barriers to each other’s success.
Conflict management Techniques
The managers of a business organization should take careful steps to resolve conflicts, otherwise organizational goals cannot be achieved in time, with the expected resources.
Managers should go for conflict stimulation, prevention, and resolution techniques. These are considered the most effective conflict management techniques in the workplace.
1. Conflict Stimulation Techniques
Conflict stimulation are those intentional actions or techniques that are employed to escalate or incite conflicts within organizations.
While conflicts are generally viewed as disruptive and undesirable, there are cases where controlled conflict can also be beneficial for promoting innovation, creativity, and improved decision-making processes.
The following four techniques are commonly used to stimulate conflicts:
a) Reorganizing
Restructuring organizational departments or units to introduce changes that create friction and conflicting interests, which will disrupt established dynamics.
b) Communication
Encouraging transparent and open communication channels to foster diverse perspectives and opinions, leading to clashes and disagreements.
c) Encouraging Competition
Introducing performance-based incentives and rewards that trigger conflict as individuals and teams strive to outperform one another.
d) Bringing in Outsiders
Engaging external consultants or experts with fresh perspectives that will challenge existing norms, thus leading to conflicts as individuals defend their positions and resist change.
2. Conflict Prevention Techniques:
In the workplace, conflict prevention techniques refer to proactive measures and strategies that are employed to minimize the occurrence and intensity of conflicts. Rather than allowing conflicts to escalate leading to disruption in the functioning of management, these techniques identify potential sources of conflict and address them before they become major problems.
a) Superordinate Goals
Emphasize the shared objectives that encourage collaboration and reduce conflicts arising from competing goals.
b) Reduce Interdependence
Restructure workflows and responsibilities to minimize reliance on conflicting parties, hence reducing potential clashes.
c) Exchange of Personnel
Exchange individuals among conflicting groups to collaborate and promote understanding.
d) Liaison Group
Establishing a forum for ongoing communication and conflict resolution among the representatives from conflicting parties.
3. Conflict Resolution Techniques
Conflict resolution is the process of addressing and resolving conflicts in a satisfactory and constructive manner. It typically involves finding mutually agreeable solutions that will meet the needs and interests of all the parties involved.
Here are four of the common conflict resolution techniques:
a) Problem-Solving
Problem-solving focuses on identifying underlying issues causing the conflict and working collaboratively on finding a solution that satisfies everyone’s interests. This technique promotes open communication, active listening, and exploration of creative alternatives
b) Accommodation
In this technique, one party is willing to yield to the other’s needs and preferences to resolve the conflict. It emphasizes on maintaining relationships and prioritizing harmony over individual desires.
c) Compromising
Compromising involves finding a middle ground where each party involved, gives up something to reach a mutually acceptable outcome. This technique requires negotiation and willingness to make concessions to reach a fair resolution.
d) Avoidance
In this case scenario, conflicts are temporarily set aside or avoided when the timing and circumstances are not conducive to resolution. While avoidance may not, however, be a long-term solution, it can surely provide a cooling-off period and allow for further reflection before addressing the conflict.
The Final Word
The meaning of conflict is a natural and inevitable outcome of every organization and as such, should be accepted. As every organization is composed of individuals having different values, goals, and perceptions, conflicts are bound to arise. Hence, conflict is unavoidable, but need not always be harmful. Under certain circumstances, it could even lead to innovative solutions to problems.
We hope you understand what is conflict means and its characteristics, types and conflict managing techniques. If you still have any queries related this guide of conflict please let us know in the comment section. we will surely help you.




2 Comments on “What is Conflict? Definition, Characteristics, Types”